SPSS Moderation Analysis Using Hayes PROCESS Macro
Moderation analysis is an advanced statistical technique used to examine when, for whom, or under what conditions an independent variable influences a dependent variable. Unlike basic regression models, moderation analysis allows researchers to test whether the strength or direction of a relationship changes depending on a third variable known as a moderator.
Students frequently encounter moderation analysis in psychology, education, business, nursing, and social science research. However, interpreting interaction effects in SPSS can be challenging without proper guidance. For students who need structured academic support, professional assistance is available through SPSS Help for Students and SPSS Data Analysis Help, where complex analyses are explained in clear, academic language.
This guide explains moderation analysis in SPSS from theory to execution, interpretation, and APA-style reporting using the Hayes PROCESS Macro.
What Is Moderation Analysis in SPSS?
Moderation analysis examines whether the effect of an independent variable (X) on a dependent variable (Y) depends on the level of another variable, called the moderator (W). In other words, moderation answers the question: does the relationship between X and Y change when W changes? This is particularly important in behavioral, social science, business, and education research, where relationships are rarely uniform across all individuals or conditions.
For example, job stress may predict employee performance, but this relationship might be weaker for employees with strong social support. In this case, social support moderates the relationship between stress and performance. SPSS moderation analysis formally tests this interaction by including an interaction term (X × W) in a regression model and evaluating whether that interaction is statistically significant.
Moderation Analysis vs Mediation Analysis
Moderation analysis is often confused with mediation analysis, but the two serve fundamentally different purposes. Mediation analysis explains how or why an independent variable affects a dependent variable by introducing a mediator that transmits the effect. Moderation analysis, on the other hand, explains when or under what conditions the effect occurs by testing whether the relationship changes across levels of a moderator.
For instance, if training improves performance because it increases motivation, motivation is a mediator. However, if training improves performance more for experienced employees than inexperienced ones, experience is a moderator. Understanding this distinction is critical for choosing the correct analysis method in SPSS and for defending your results during assessment or dissertation review.
When Should You Use Moderation Analysis?
Moderation analysis should be used when your research question or hypothesis explicitly suggests that a relationship may not be consistent across all cases. This often appears in hypotheses using language such as “depends on,” “varies by,” “is stronger when,” or “is weaker under certain conditions.” Moderation is common in psychology, management, education, health sciences, and marketing research.
Researchers typically use moderation analysis when they want to examine interaction effects, conditional relationships, or subgroup differences within regression frameworks. If your theoretical framework suggests that a variable influences the strength or direction of another relationship, moderation analysis is the appropriate statistical approach.
Hayes PROCESS Macro for Moderation Analysis
The Hayes PROCESS Macro is a widely accepted SPSS extension developed by Andrew F. Hayes to perform mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. It is especially popular because it automates complex regression steps, generates interaction terms correctly, and provides bootstrap confidence intervals that are more robust than traditional significance tests.
For moderation analysis, PROCESS Model 1 is most commonly used. This model estimates the direct effect of X on Y, the effect of the moderator W, and the interaction effect between X and W. The macro also produces conditional effects at different values of the moderator, allowing researchers to interpret how the relationship changes across low, medium, and high levels of W.
How to Install Hayes PROCESS Macro in SPSS
To conduct moderation analysis using PROCESS, the macro must first be installed in SPSS. This involves downloading the correct version of the macro that matches your SPSS software and installing it through the SPSS syntax editor. Once installed, the PROCESS Macro appears under the Analyze > Regression menu, making it accessible like any built-in SPSS procedure.
Correct installation is essential because an outdated or incompatible version can lead to errors or incomplete output. Researchers should always confirm that PROCESS appears in the SPSS menu before attempting to run moderation analysis.
Assumptions of Moderation Analysis
Moderation analysis relies on the assumptions of multiple regression. These include linear relationships between variables, independence of observations, normally distributed residuals, and homoscedasticity. Additionally, moderation analysis requires particular attention to multicollinearity, as interaction terms can inflate correlations between predictors.
To reduce multicollinearity, researchers often mean-center the independent variable and the moderator before creating the interaction term. Mean-centering does not affect significance results but improves the interpretability and numerical stability of the model. Ignoring these assumptions can result in misleading conclusions, even if the interaction term appears statistically significant.
Hypotheses in Moderation Analysis
Moderation analysis focuses on the hypothesis that the interaction between X and W significantly predicts Y. The null hypothesis states that the interaction effect is zero, meaning the relationship between X and Y does not change across levels of W. The alternative hypothesis states that the interaction is non-zero, indicating a moderation effect.
Importantly, a significant moderation effect can exist even when the main effects of X or W are not significant. Therefore, interpretation should prioritize the interaction term rather than focusing solely on direct effects.
Step-by-Step Moderation Analysis in SPSS Using PROCESS
Running moderation analysis in SPSS using PROCESS involves preparing your dataset, opening the PROCESS dialog box, and correctly assigning variables. The independent variable is placed in the X field, the dependent variable in the Y field, and the moderator in the W field. Model 1 is selected for simple moderation, and bootstrap samples are typically set to 5,000 to ensure stable confidence intervals.
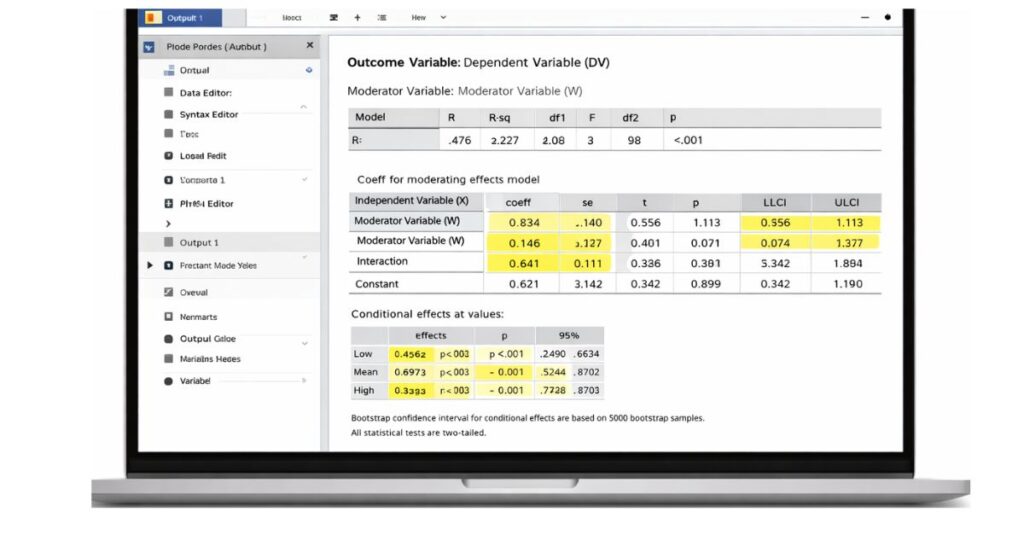
Once the analysis is run, SPSS produces output tables that include the regression coefficients, interaction term significance, and conditional effects. Each of these outputs must be interpreted carefully to draw correct conclusions about moderation.
Understanding SPSS Output for Moderation Analysis
The most important part of moderation analysis output is the interaction term. A statistically significant interaction indicates that the effect of X on Y varies across levels of the moderator. SPSS also provides conditional effects, showing how the relationship changes at low, medium, and high levels of W.
Bootstrap confidence intervals are particularly important because they determine whether the interaction effect is statistically reliable. If the confidence interval does not include zero, the moderation effect is considered significant.
Simple Slopes and Interaction Interpretation
Simple slopes analysis helps explain how the relationship between X and Y behaves at specific levels of the moderator. Rather than reporting a single regression coefficient, researchers describe how the effect changes when the moderator is low, average, or high.
This interpretation is crucial for making results meaningful. Instead of stating that moderation exists, researchers explain how and why the relationship changes, which strengthens theoretical contributions and practical implications.
How to Report Moderation Analysis in APA Style
APA reporting of moderation analysis requires clear presentation of the interaction effect, including regression coefficients, standard errors, p-values, and confidence intervals. Researchers should also report conditional effects and describe the nature of the interaction in words.
A well-written APA report ensures that readers understand not only whether moderation exists, but also how the moderator influences the relationship. This clarity is especially important for dissertations and journal submissions.
Common Mistakes Students Make in Moderation Analysis
Students often make errors such as ignoring the interaction term, failing to mean-center variables, or misinterpreting main effects instead of focusing on moderation. Another common mistake is reporting p-values without explaining the direction or meaning of the interaction.
Avoiding these mistakes significantly improves the quality, credibility, and grading outcome of SPSS moderation analysis results.
Example of Moderation Analysis
Consider a study examining whether workload predicts burnout differently depending on social support. Moderation analysis may reveal that workload strongly predicts burnout when social support is low, but the relationship weakens when support is high. This result demonstrates a buffering effect, where the moderator reduces the negative impact of the independent variable.
Such examples help translate statistical output into real-world meaning and strengthen academic arguments.
Get Professional Help With SPSS Moderation Analysis
Moderation analysis can be complex, especially when interpreting interaction effects and reporting results correctly. Professional SPSS support ensures that analyses are accurate, assumptions are met, and results are written in proper academic language.
If you need help with moderation analysis for assignments, dissertations, or research projects, expert SPSS assistance can save time, reduce errors, and improve your final outcome.